Study of the Effect of Thyroid Disorders on Reproductive Function in a Sample of Infertile Women
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63318/waujpasv3i2_01Keywords:
Thyroid disorders, Infertility in women, Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Reproductive functionAbstract
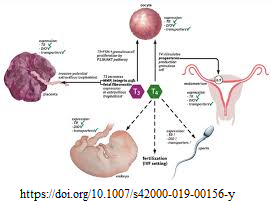
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of thyroid disorders on fertility in women. The
study included 210 women between the ages of 25 and 45 years. Participants were divided into
three groups. The first group included 120 women previously diagnosed with thyroid disorders,
including 60 women with hypothyroidism and 60 women with hyperthyroidism. The second group
included 30 healthy women who served as a control group. The third group included 60 pregnant
women with thyroid disorders, 30 women with hypothyroidism, and 30 women with
hyperthyroidism. The cases were followed to identify fetal problems resulting from thyroid
disorders during pregnancy and after delivery. Levels of thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3),
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone
(FSH), and prolactin (PRL) were determined. The results showed significant differences between
healthy women and women with hypothyroidism in level of PRL (P≤0.05), FSH (P≤0.05), and LH
(P≤0.05). No significant differences were found between healthy women and women with
hyperthyroidism. The regression analysis results showed that in cases of hypothyroidism, thyroid
hormones affected FSH (P≤0.05), LH (P≤0.05), and PRL (P≤0.05), with decreased FSH and LH
levels and increased PRL level. In cases of hyperthyroidism, thyroid hormones affected LH
(P≤0.05), leading to an increase in LH level, while FSH and PRL levels remained
normal.Therefore, thyroid dysfunction may be a major hormonal factor in fertility problems, and
therefore, thyroid hormone assessment is very important in pregnancy monitoring and in the
treatment of infertile women.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This journal uses Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommerical 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
Copyright of articles
Authors retain copyright of their articles published in this journal.




