The Impact of Loss of Power Supply Probability on Design and Performance of Wind/ Pumped Hydropower Energy Storage Hybrid System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63318/waujpasv3i2_06Keywords:
Pumped hydropower storage, Hybrid renewable energy, Wind energy, Sizing optimizationAbstract
Hybrid renewable energy systems is broadly adopted because they are eco- friendly systems. The
general electric grid in Libya has suffered from shortage during the recent years . However , Libya
has formidable opportunities for investment in clean energy .Their wind energy resources are
promising. The southern region of Libya has demonstrated the viability of utilizing pumped
hydroelectric and wind energy for electricity generation, thereby addressing the deficit and
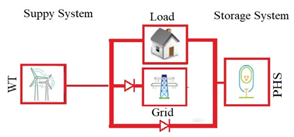
strengthening the resilience of the public grid. In this study, hybrid renewable energy system
(HRES) consists of 432 MW of wind energy farm and 10782 MWh of pumped hydropower system
has been designed, analyzed and optimized to meet a demand of 590,019 MWh. The decision to
design these systems is strongly affected by energy prices and pollution. The impact of the Loss
Power Supply Probability (LPSP) and the cost of CO2 emissions on the levelized cost of energy
(LCOE) is loss discussed
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This journal uses Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommerical 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
Copyright of articles
Authors retain copyright of their articles published in this journal.




