Impact of Dielectric Substrate Material on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antennas (MPAs), V-Band
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63318/waujpasv4i1_14Keywords:
5G Applications, Dielectric constant, Microstrip patch antenna (MPA), Millimeter wave (mm Wave), Substrate material, V-BandAbstract
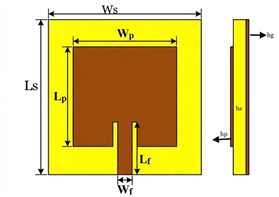
Microstrip Patch Antennas (MPAs) are pivotal components in modern communication systems due to their compact size and ease of fabrication; however, the shift toward the V-band necessitates designs that ensure high gain and efficiency despite challenges related to dielectric loss and narrow bandwidth. This paper analyzes the impact of substrate material properties—specifically dielectric constant and loss—on the performance of an MPA designed for a 55 GHz center frequency within the 50–60 GHz band. Using CST Microwave Studio, the antenna was simulated with uniform dimensions on three Rogers substrates of 0.127 mm thickness: RT/duroid 5880, RO3003, and RO4350B, evaluating gain, efficiency, reflection coefficient (S11), and bandwidth. Simulation results revealed distinct performance variations; the RT/duroid 5880 model (lowest permittivity) achieved the highest gain (6.16 dBi) and directivity (6.82 dBi), making it ideal for long-range applications, while the Rogers RO4350B recorded the highest radiation efficiency (89.6%). Conversely, the Rogers RO3003 model demonstrated the best impedance matching (S11 -19.8 dB) and the widest bandwidth (2.527 GHz). Consequently, the study concludes that optimal material selection depends on specific application priorities, recommending the RO3003 substrate as the premier choice for 5G applications requiring ultra-high data transfer rates due to its superior bandwidth performance.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This journal uses Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommerical 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
Copyright of articles
Authors retain copyright of their articles published in this journal.




